Language of Data Entry
While the user interface of the program is entirely in English, regional and language settings on a Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Window Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, or Windows Server 2008 R2 workstation may be configured to enter data in one or more of the following additional languages: Afrikaans, Albanian, Alsatian, Arabic, Azeri (Azerbaijani), Bashkir, Basque, Belarusian, Bosnian, Breton, Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese, Corsican, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dari, Dutch, Estonian, Faeroese, Filipino, Finnish, French, Galician, German, Greek, Greenlandic, Hausa, Hebrew, Hungarian, Icelandic, Igbo, Indonesian, Inuktitut, Irish, Italian, Japanese, Kazakh, K’iche, Kinyarwanda, Korean, Kyrgyz (Kirghiz), Latvian, Lithuanian, Lower Sorbian, Luxembourgish, Macedonian, Malay, Maltese, Maori, Mapudungun, Mohawk, Mongolian, Sesotho (Northern Sesotho, Sesotho sa Leboa), Norwegian, Occitan, Persian (Farsi), Polish, Portuguese, Quechua, Romanian, Romanish, Russian, Sami, Serbian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Swahili (Kiswahili), Swedish, Tajik, Tamazight, Tatar, Thai, Tswana (Setswana), Turkish, Turkmen, Uighur, Upper Sorbian, Ukrainian, Urdu, Uzbek, Vietnamese, Welsh, Wolof, Xhosa (isiXhosa), Yakut, Yoruba, or Zulu (isiZulu). Most custom heading and field captions may also be renamed to their foreign-language equivalents (see Custom Captions).
Many of the above languages that are based on the Latin alphabet require no language settings to be configured under Windows (e.g. French, Spanish) However, many languages use extensions of the Latin alphabet (e.g. Vietnamese), other alphabet systems (e.g. Russian), symbols (e.g. Chinese), scripts (e.g. Hindi), or require that the characters be written from right-to-left (e.g. Arabic). The universal way of handling this great variety of languages is with a technology called Unicode. Unicode allows data to be entered, stored, and printed in any combination of languages. While At Your Service supports native Unicode databases and native Unicode printing, the data entry interface does not natively support Unicode and therefore requires Windows to be configured to correctly interpret some languages.
While there is support for Unicode in some of the earlier Windows operating systems, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, or Windows Server 2008 R2 is recommended for support of the above-listed languages. In addition to languages based on the basic Latin alphabet (e.g. English, French, Spanish), Windows can be configured to support one additional language. If there are other languages closely related to the selected language then they can usually be entered as well. For example, selecting a language that uses the Cyrillic alphabet (e.g. Russian) will generally allow support for any language that uses that alphabet (e.g. Bulgarian, Ukrainian). Additionally, the above list of languages includes only those that are officially supported by Microsoft. Other languages not listed, but that use the same alphabet system as one of the listed languages, may be entered by selecting a language with a similar alphabet system.
To configure Windows to support an additional language, open Regional and Language Options in the Windows control panel and select the Advanced tab.
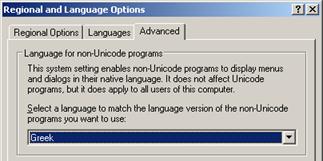
Select the desired language and click the OK button.
NOTE Since support for languages that are not based on the basic Latin alphabet is provided directly by the Windows operating system, some data entry fields may interact differently than the way that they do with the English language. Further, some languages, particularly script languages (e.g. Hindi), cannot be interpreted by Windows for programs that do not have native Unicode support. These languages include, among others, Amharic, Armenian, Assamese, Bengali, Divehi, Georgian, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Khmer, Konkani, Lao, Malayalam, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Pashto, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Sinhala, Syriac, Tamil, Telugu, Tibetan, and Yi. Therefore data may not be entered into the program in those languages.
NOTE While the above instructions are specifically for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, they will be very similar for Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 R2.
Right-to-Left Languages
In order to support languages that are written from right-to-left (i.e. Arabic, Hebrew, Farsi, Urdu) Windows may require the installation of additional files before allowing the language to be selected. Open Regional and Language Options in the Windows control panel and select the Languages tab. Select the checkbox next to Install files for complex script and right-to-left languages (including Thai) and click the OK button.
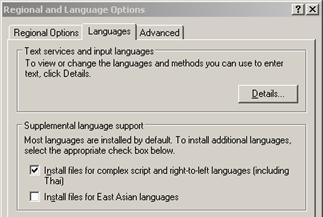
NOTE While data entry of characters within the individual fields will be from right-to-left, the positioning of the fields themselves on entry screens and printouts will continue to be on the left side of the screen or the left side of the printout.
NOTE The above instructions are specifically for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 R2 install all of the languages by default.
Oriental Languages
In order to support oriental languages (i.e. Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Thai, Vietnamese) Windows may require the installation of additional files before allowing the language to be selected. Open Regional and Language Options in the Windows control panel and select the Languages tab. For the Thai and Vietnamese languages, select the checkbox next to Install files for complex script and right-to-left languages (including Thai) and click the OK button. For the Chinese, Japanese, and Korean languages, select the checkbox next to Install files for East Asian languages and click the OK button.
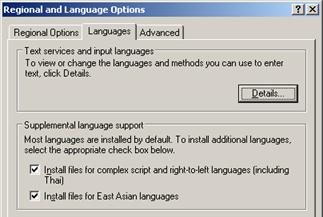
Due to the complexity of the Chinese and Japanese
languages, they also require further programming support within the At Your
Service program in additional to the configuring of the Windows regional and
language options. To enable support for the Chinese language within At Your
Service, first close all windows within the main program shell and then select
Setup  Language
Language  Allow Data Entry of Chinese
Characters. Similarly, to enable support for the Japanese language within At
Your Service, first close all windows within the main program shell and then
select Setup
Allow Data Entry of Chinese
Characters. Similarly, to enable support for the Japanese language within At
Your Service, first close all windows within the main program shell and then
select Setup  Language
Language  Allow Data Entry of Japanese
Characters. Selecting the same option again disables the setting.
Allow Data Entry of Japanese
Characters. Selecting the same option again disables the setting.
Support for the Chinese and Japanese languages is available only on Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 R2 operating systems, and only for licensed users of version 2.6 and higher.
NOTE The above instructions are specifically for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 R2 install all of the languages by default.
NOTE Some oriental languages interpret the backslash (\) character using the Won (₩) symbol or the Yen (¥) symbol. This will be particularly visible in file paths, such as the path to your At Your Service Microsoft Access database. While it is not visually esthetic, this behavior is normal and can be ignored.
 Language of Communication
Language of Communication