Automatically Backing Up an Access Database
Three backup copies of each Access database can be maintained automatically in the background. Timed backups can be made at a frequency varying from every 5 minutes to every 8 hours and stored in a specified folder on the network. Additionally, each morning a daily backup is stored in another specified folder on the network, and the previous day’s backup is transferred to a secondary backup file.
TIP It is also highly recommended that a regular daily, weekly, or monthly backup of all data be made to removable backup media (e.g. CD, DVD, external hard drive, tape, USB drive; see Saving a Backup Copy of an Access Database, and Saving a Zipped Backup Copy of an Access Database). Some of these backup copies should be stored off-site to protect your data in the case of theft or fire.
To configure automatic backups, first close all windows
within the main program shell and then select File  AutoBackup Database from the main
menu. Only the program administrator (see User
Security) can configure automatic backups. Enter automatic backup settings
and click the Save button to save changes. Click the Close/Cancel
button or press the Esc key to quit without saving changes.
AutoBackup Database from the main
menu. Only the program administrator (see User
Security) can configure automatic backups. Enter automatic backup settings
and click the Save button to save changes. Click the Close/Cancel
button or press the Esc key to quit without saving changes.
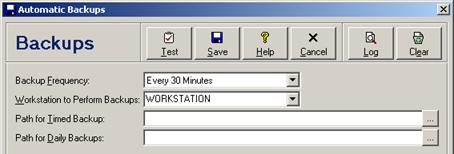
Each automatic backup option is discussed in the following table.
Automatic Backup Entry Fields
|
Field |
Description |
|
Backup Frequency |
Select the frequency (in minutes or hours) with which the open database should be periodically backed up, or select No Backups to disable automatic timed backups. The default is every 30 minutes. |
|
Backup only from Workstation |
Enter or select the workstation name of the physical workstation that is running At Your Service – Repair Centre that should perform the backup. By default, the first workstation that opens a new database is automatically configured as the workstation to perform the backup. Only names of workstations that have previously opened the current database will appear in the dropdown list. To reduce network traffic, it is recommended that either the workstation where the open database is physically located or the workstation where the backups are to be stored perform all backups. Additionally, it should be a workstation that is always running At Your Service – Repair Centre since the software must be running for the backups to start. The user whose workstation is performing the backup must have network access rights to the backup folders (see below). A warning message will appear when saving if the selected workstation is different from the current workstation. |
|
Path for Timed Backup |
Enter the folder where periodic backups are to be stored, or click the … button to navigate and select a folder. On a network, the folder name will automatically be formatted using the universal naming convention (i.e. \\servername\pathname). If left empty then the timed backup will be stored in the same folder as the open database. The user whose workstation is performing the backup must have network access rights to the specified folder. To reduce network traffic, it is recommended that this folder be on the same physical workstation as the open database. |
|
Path for Daily Backups |
Enter the folder where both the daily backup and the previous day’s backup are to be stored, or click the … button to navigate and select a folder. On a network, the folder name will automatically be formatted using the universal naming convention (i.e. \\servername\pathname). If left empty then the daily backups will be stored in the same folder as the open database. The user whose workstation is performing the backup must have network rights to the specified folder. For protection from physical damage to or loss of the workstation where the open database is located (e.g. theft, fire, hard drive failure), it is recommended that daily backups be stored in a folder on a different physical workstation. |
NOTE A common mistake when moving an At Your Service installation from one workstation to another is to forget to change the name of the workstation that is to perform the backup to the name of the new workstation. A related problem occurs when one or both of the backup paths point to a folder that no longer exists or is blocked by network security, or to a workstation that has been renamed. Therefore when saving or testing automatic backup settings, a warning message will appear if the selected workstation is different from the current workstation. Similarly, on the workstation configured to perform the automatic backups, a warning message will appear when starting the program and when saving automatic backup settings if either of the backup paths are currently invalid or cannot be accessed.
A  icon will be displayed in the
status bar (see Status Bar) any time that backups
are disabled on the current workstation, either because of one of the above
problems, or because the backup frequency was set to no backups.
icon will be displayed in the
status bar (see Status Bar) any time that backups
are disabled on the current workstation, either because of one of the above
problems, or because the backup frequency was set to no backups.
Automatic background database backups are not available for MySQL or Microsoft SQL Server databases.
(See also Saving a Backup Copy of an Access Database, and Saving a Zipped Backup Copy of an Access Database.)
Backup Verification
Each time a backup is attempted, a  icon will appear briefly in the status bar
until the backup has either completed or failed (see Status Bar). Click the Test button to test the
timed backup immediately and watch for the disk icon to appear briefly. Since
the test should ideally be performed from the same workstation that is
configured to process the automatic backups, a warning message will appear if
the selected workstation is different from the current workstation.
icon will appear briefly in the status bar
until the backup has either completed or failed (see Status Bar). Click the Test button to test the
timed backup immediately and watch for the disk icon to appear briefly. Since
the test should ideally be performed from the same workstation that is
configured to process the automatic backups, a warning message will appear if
the selected workstation is different from the current workstation.
A detailed log is recorded of each backup attempt including whether or not it was successful. Click the Log button to view the log file. The most recent backups will be at the bottom of the log file. Click the Clear button to clear the log file.
Restoring a Database Backup
Timed backups are stored with a .ay1 file extension, the daily backup of yesterday’s data is stored with a .ay2 file extension, and the daily backup of data from the day before that is stored with a .ay3 file extension. In the rare case that a database ever becomes corrupted (e.g. after a power failure or system or network crash) and it cannot be repaired (see Repairing and Compacting an Access Database, and Repairing a Database) then within Windows Explorer delete the original database file and rename the most recent good backup file to a .ays extension.
See also Restoring a Backup Database for more information on using the At Your Service – Database Repair Utility to restore an automatically backed up database.
 Repairing and Compacting an Access
Database
Repairing and Compacting an Access
Database